F Appendix 6: Sylviculture simulations
F.1 Ecosystem functions
This appendix presents ecosystem resilience after 600 years with taxonomic and functional diversity after selective logging. It encompass all functionnal diversity components (FRIC, FEve, FDiv, and FDis, Villéger et al. 2008). And it presents results for both forest structure (Figure F.1) and forest functionning (Figure F.2).
![Ecosystem resilience after 600 years with taxonomic and functional diversity. Cummulative integral from ecosystem distance to forest structure equilibrium after 600 years normalized by disturbed basal area was represented against functional functional diversity [FRIC, FEve, FDiv, and FDis, @villeger_new_2008]. Dot color represents the species richness (nb) whereas dot size represents the disturbed basal area (m2/ha). Grey line represents the linear regression and grey area the confidence interval.](master-thesis_files/figure-html/A6IeqStructureAll-1.png)
Figure F.1: Ecosystem resilience after 600 years with taxonomic and functional diversity. Cummulative integral from ecosystem distance to forest structure equilibrium after 600 years normalized by disturbed basal area was represented against functional functional diversity (FRIC, FEve, FDiv, and FDis, Villéger et al. 2008). Dot color represents the species richness (nb) whereas dot size represents the disturbed basal area (m2/ha). Grey line represents the linear regression and grey area the confidence interval.
![Ecosystem resilience after 600 years with taxonomic and functional diversity. Cummulative integral from ecosystem distance to forest functionning equilibrium after 600 years normalized by disturbed basal area was represented against functional functional diversity [FRIC, FEve, FDiv, and FDis, @villeger_new_2008]. Dot color represents the species richness (nb) whereas dot size represents the disturbed basal area (m2/ha). Grey line represents the linear regression and grey area the confidence interval.](master-thesis_files/figure-html/A6IeqProductionAll-1.png)
Figure F.2: Ecosystem resilience after 600 years with taxonomic and functional diversity. Cummulative integral from ecosystem distance to forest functionning equilibrium after 600 years normalized by disturbed basal area was represented against functional functional diversity (FRIC, FEve, FDiv, and FDis, Villéger et al. 2008). Dot color represents the species richness (nb) whereas dot size represents the disturbed basal area (m2/ha). Grey line represents the linear regression and grey area the confidence interval.
F.2 Biodiversity effect
Figure F.3 presents the resilience of complementarity and selection effects for different ecosystem metrics (AGB, BA, N, GPP and NPP).
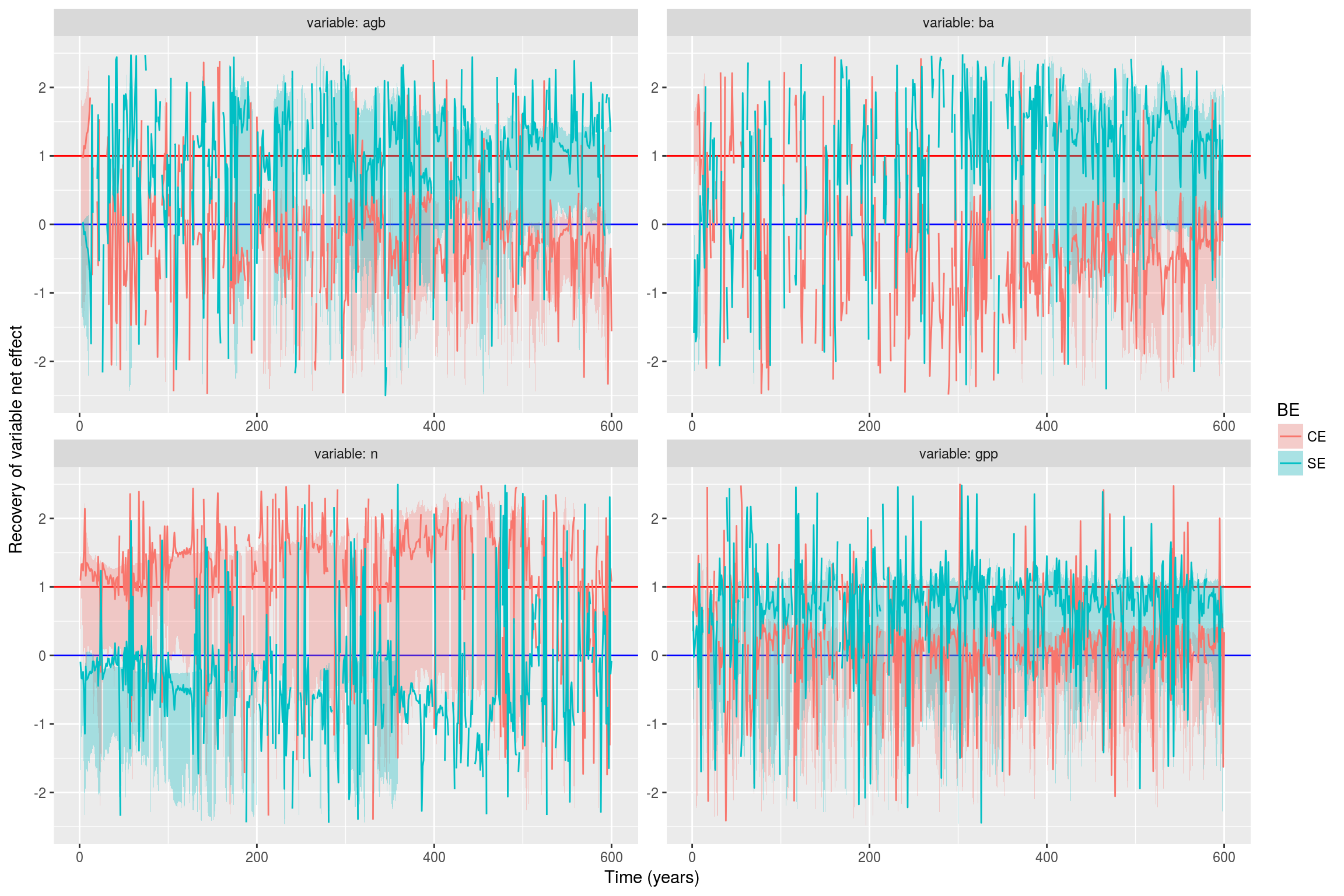
Figure F.3: Resilience of complementarity and selection effects. Complementarity effect (CE) and selection effect (SE) where normalized by control net effect (NEc), thus measuring their resilience over time for different ecosystem variables (AGB, BA, N, GPP).
References
Villéger, S., Mason, N.W.H. & Mouillot, D. (2008). New multidimensional functional diversity indices for a multifaceted framework in functional ecology. Ecology, 89, 2290–2301.