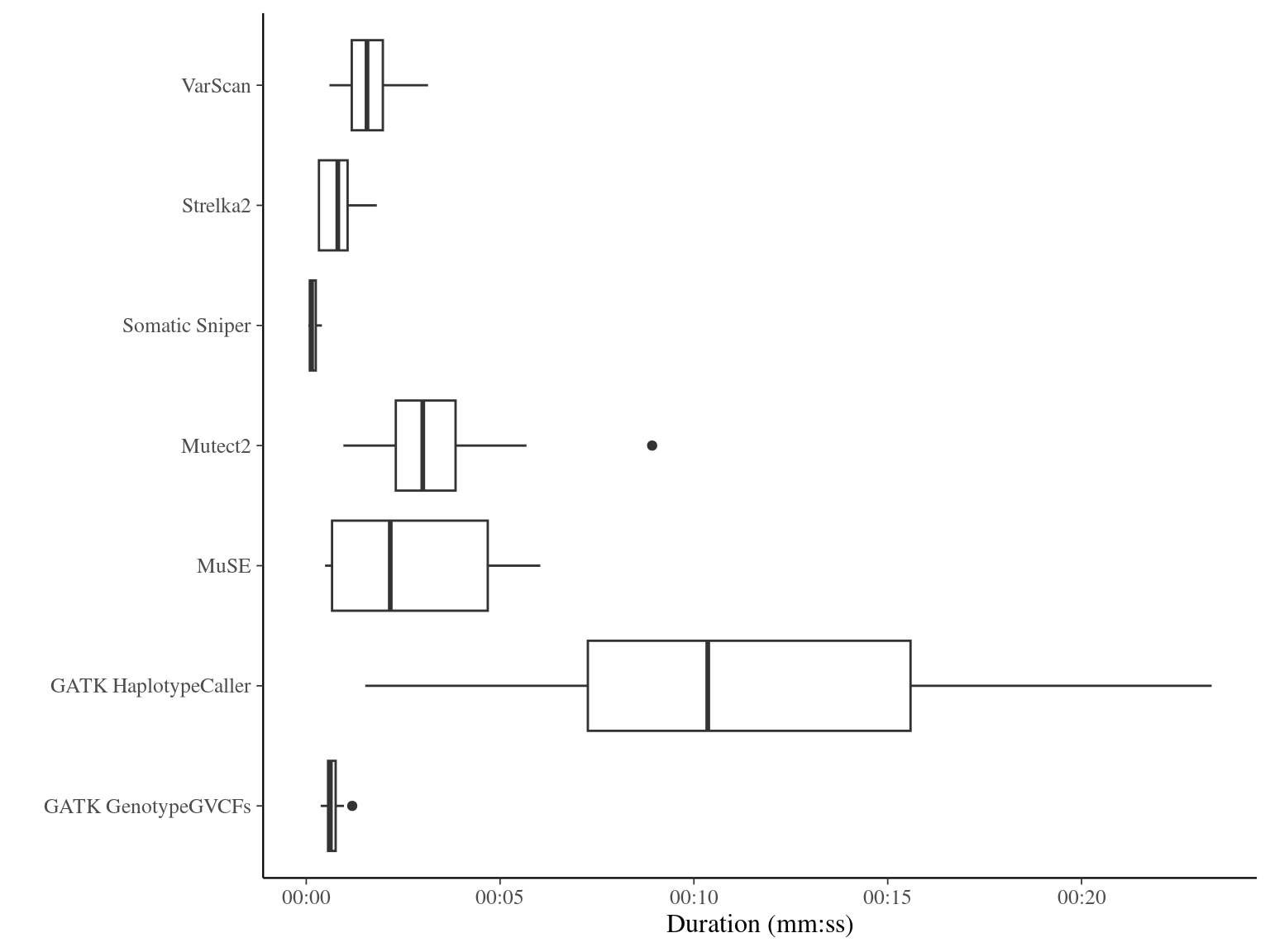
Chapter 7 Mutations in silico
This chapter described the in silico experiment using the generateMutations and the detectMutations workflows to test the effect of coverage/sequencing depth and allelic frequency on the performance of 7 tools to detect mutations either generalist or specific to mutations. Report to the published manuscript: https://peercommunityjournal.org/articles/10.24072/pcjournal.187/
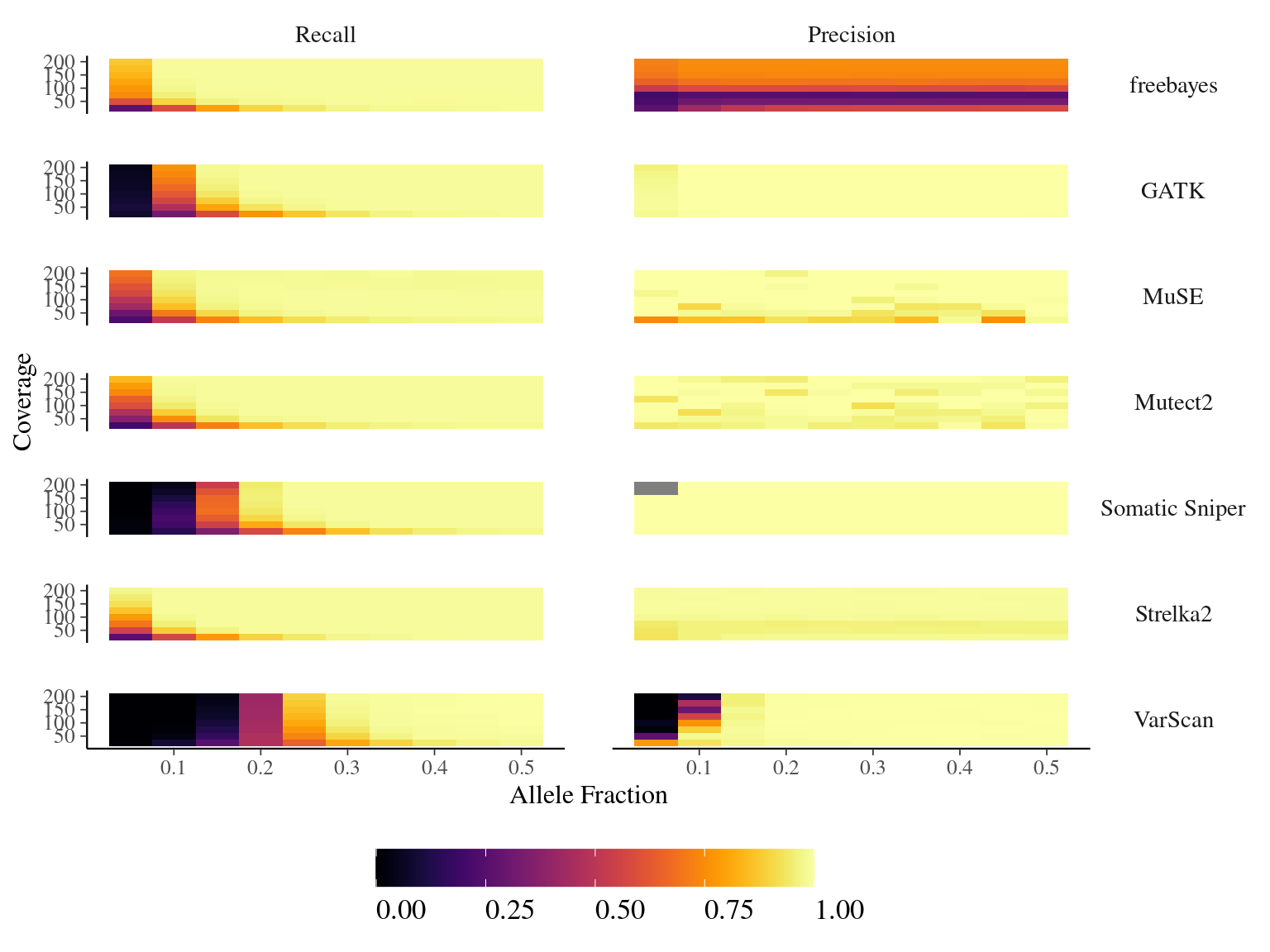
Figure 7.1: Performance of mutation detection tools with allelic fraction and coverage. The inferno, black to yellow, colour scale indicates the recall and the precision rates for each tool to detect mutations.
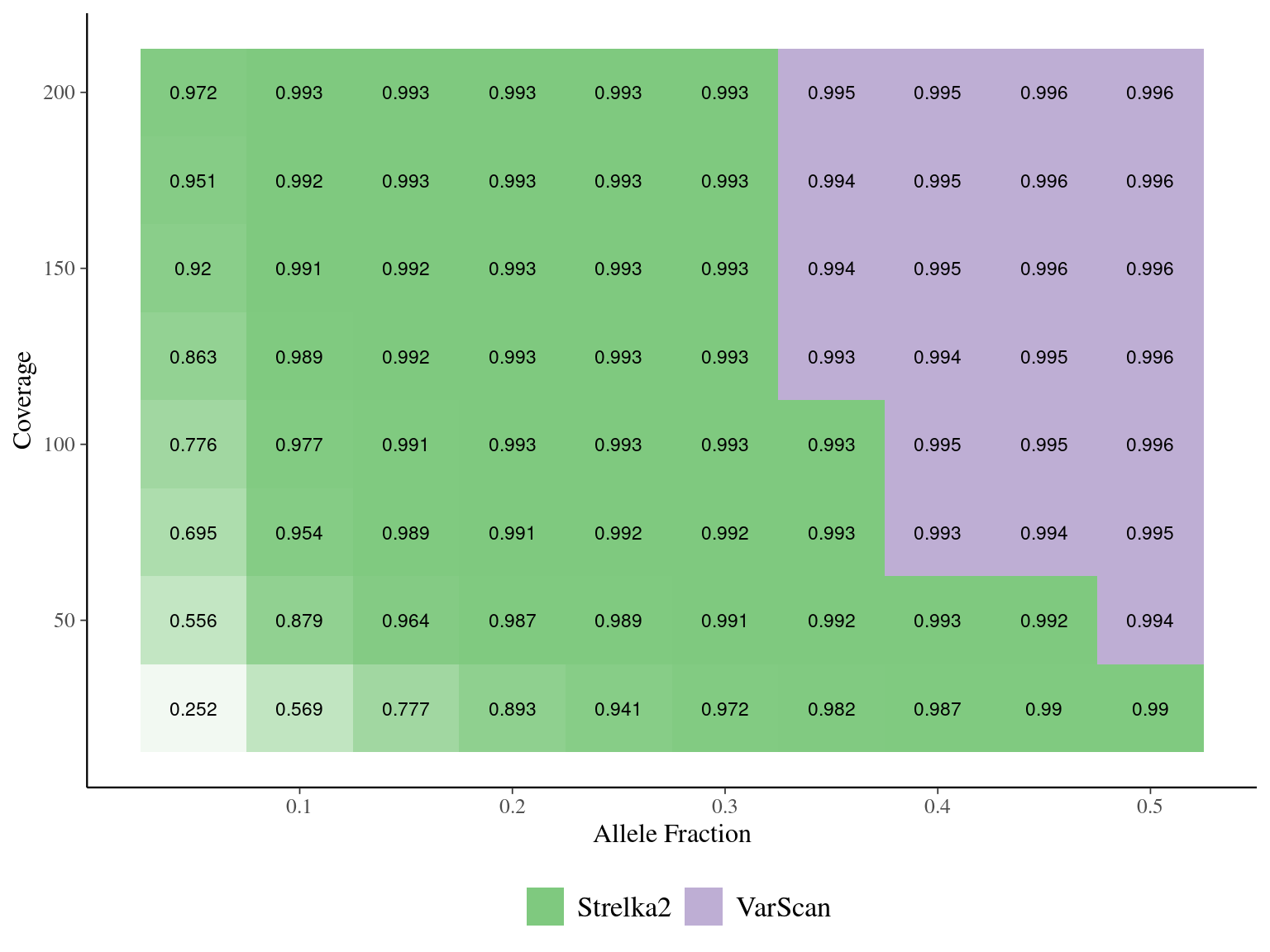
Figure 7.2: Best performing mutation detection tools depending on allelic fraction and coverage. The best performing tools were defined on the best recall rate first and best precision rate second for precision rates above 0.9. The labels in white indicate the recall rate (R) and the precision rate (P) for the best performing tools.
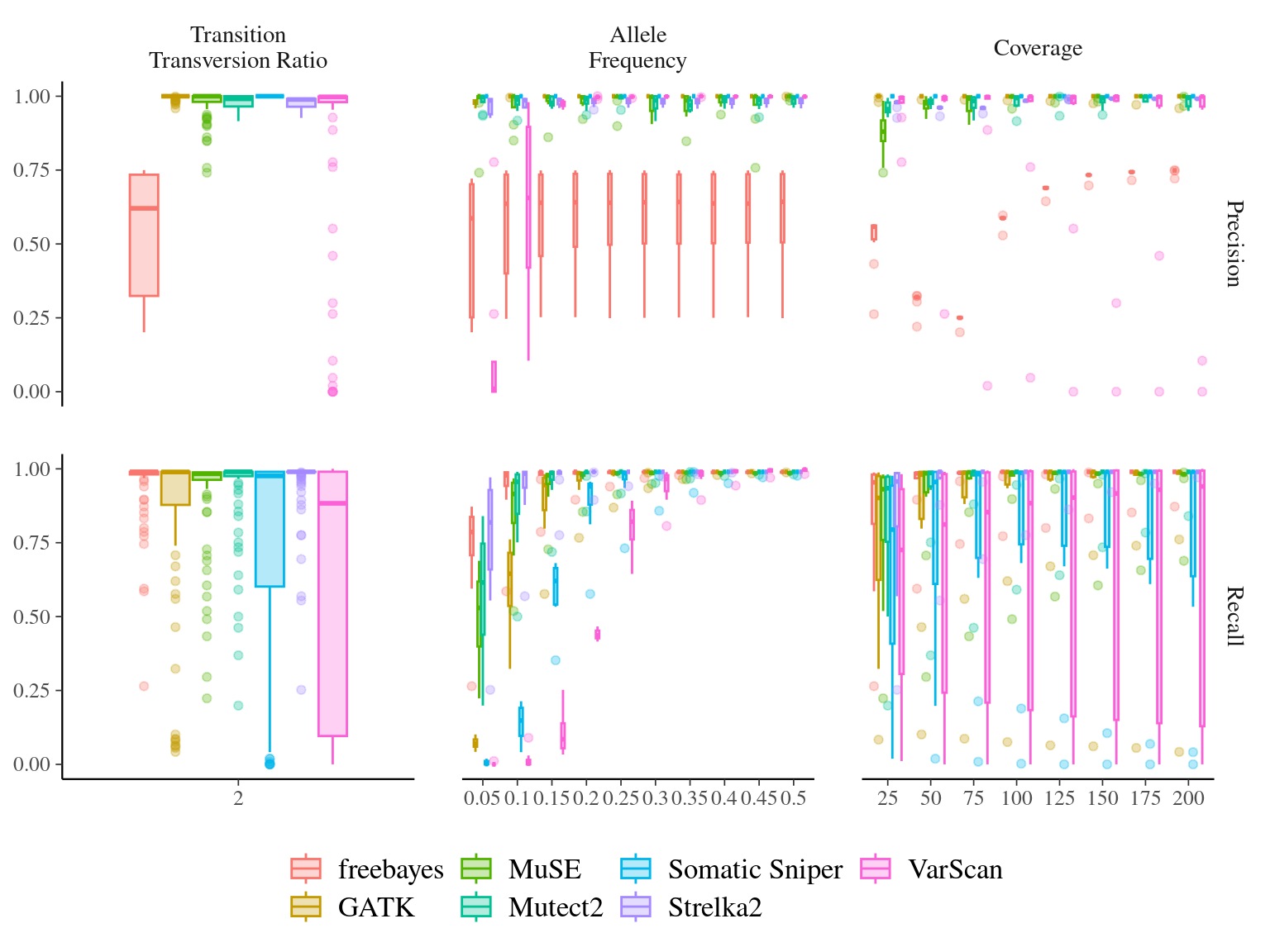
Figure 7.3: Variation in the performance of mutation detection tools with varying biological and sequencing parameters. The recall and the precision rates have been assessed for each tool to detect mutations with varying transition/transversion ratio, allelic fraction, and coverage. Tools to detect mutations include freebayes (red), MuSE (light green), Somatic Sniper (light blue), VarScan (pink), GATK (orange), Mutect2 (dark green), and Strelka2 (purple).
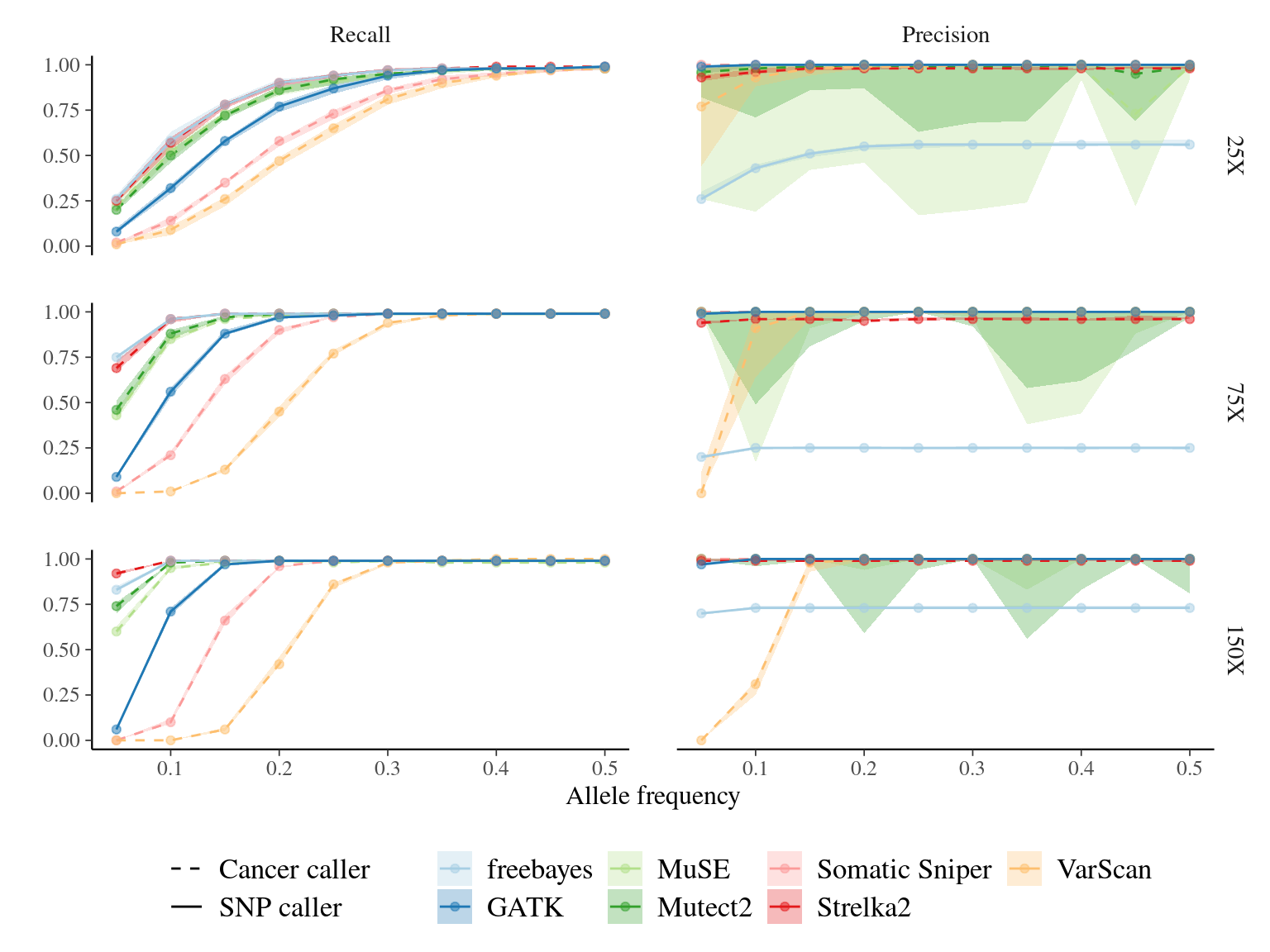
Figure 7.4: Variation in the performance of mutation detection tools with varying biological and sequencing parameters. The recall and the precision rates have been assessed for each tool to detect mutations with varying transition/transversion ratio, allelic fraction, and coverage.
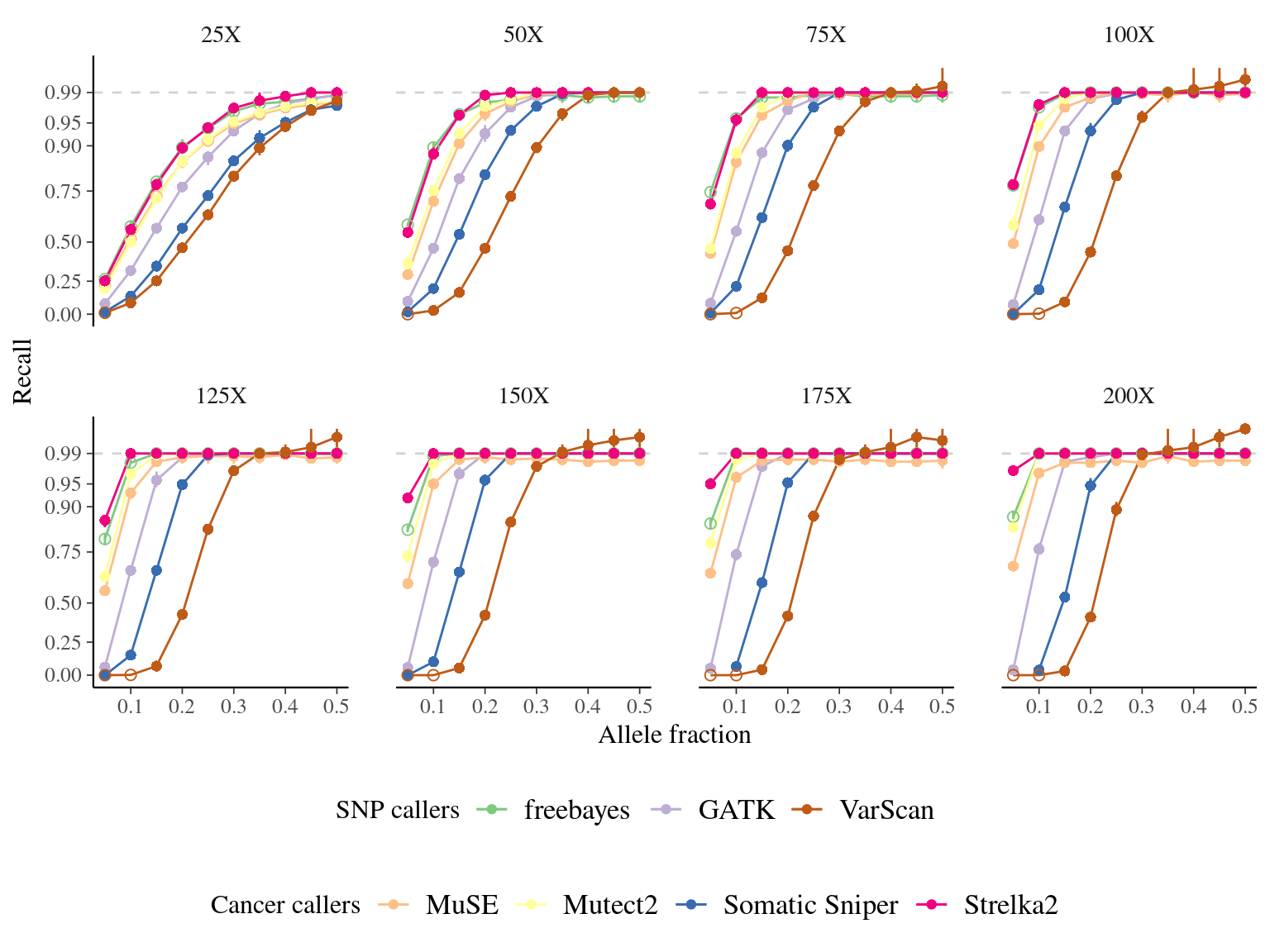
Figure 7.5: Variation in the performance of mutation detection tools with varying biological and sequencing parameters. The recall and the precision rates have been assessed for each tool to detect mutations with varying transition/transversion ratio, allelic fraction, and coverage.
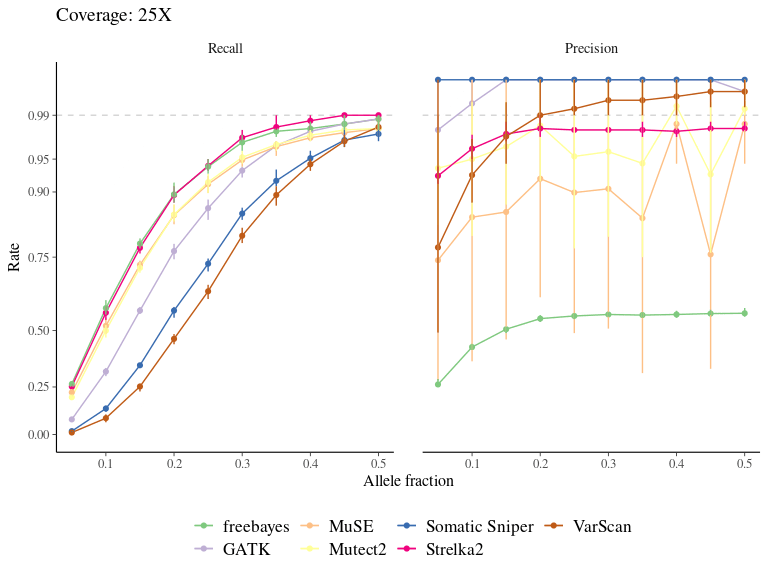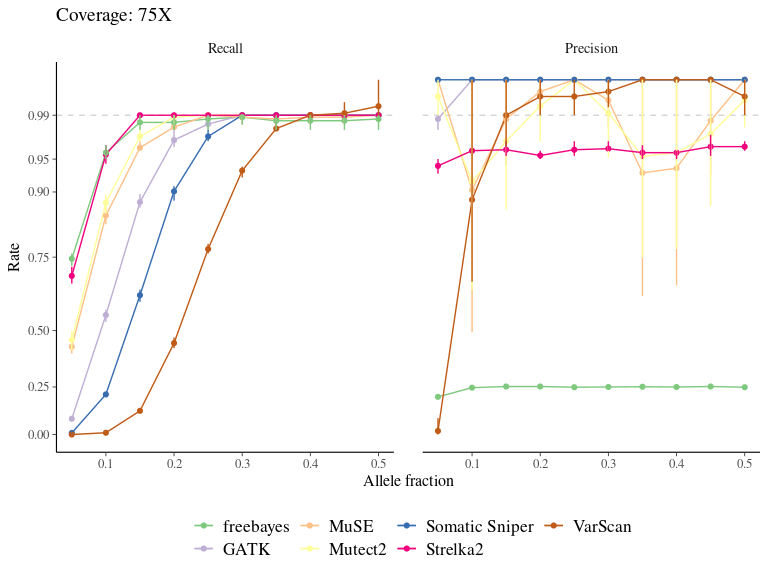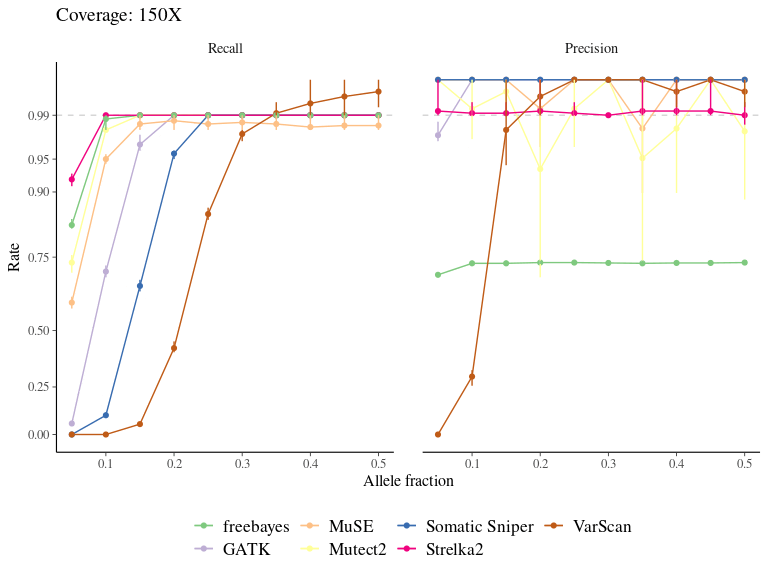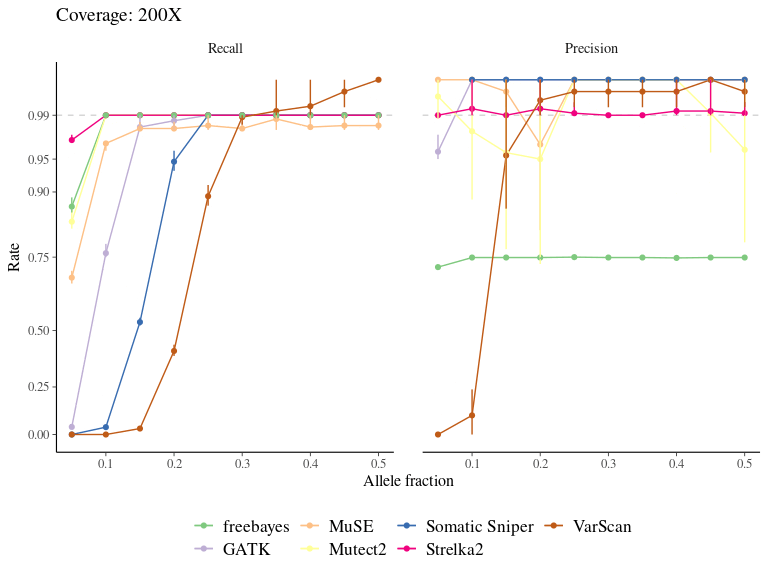
Figure 7.6: Variation in the performance of mutation detection tools with varying biological and sequencing parameters. The recall and the precision rates have been assessed for each tool to detect mutations with varying transition/transversion ratio, allelic fraction, and coverage.
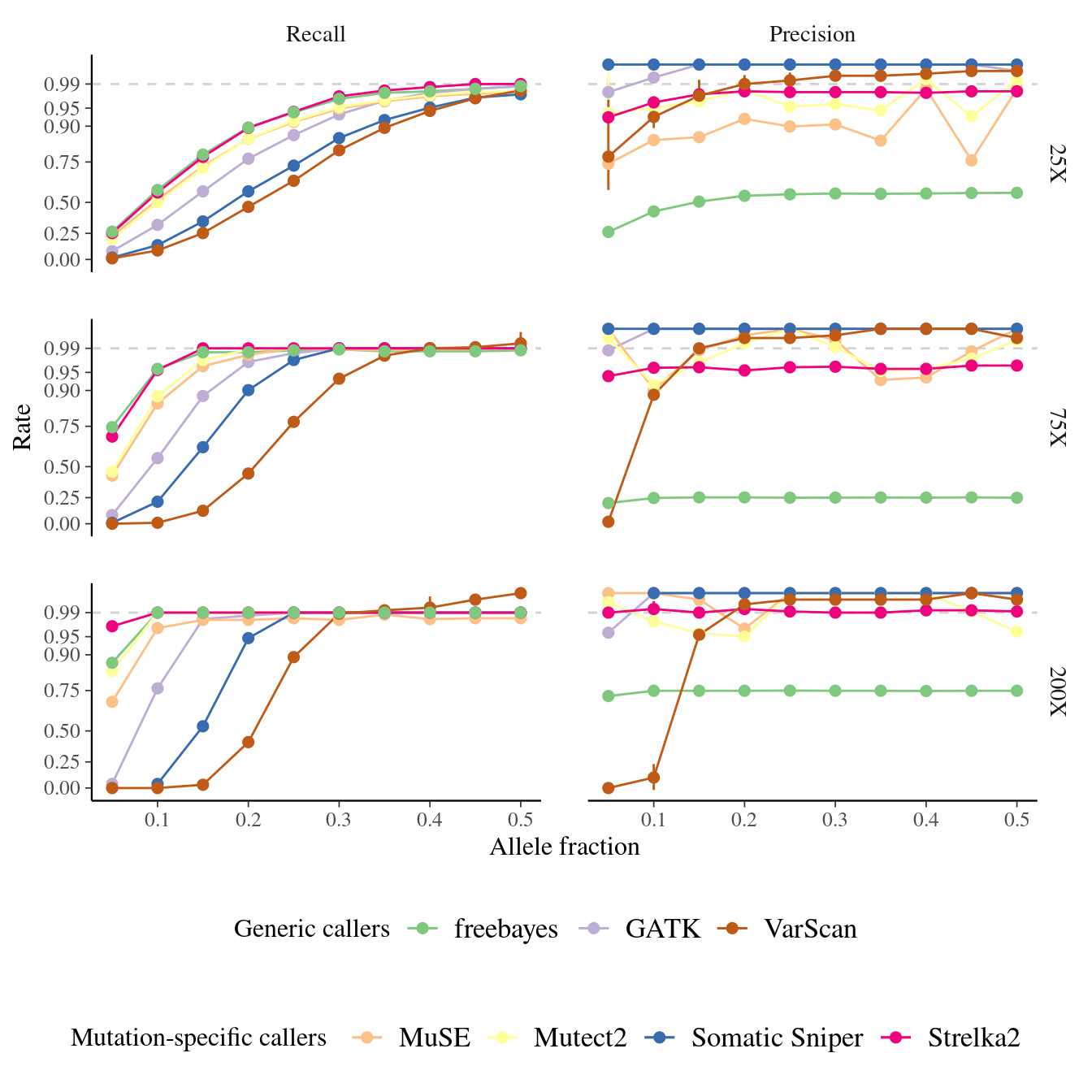
Figure 7.7: Variation in the performance of mutation detection tools with varying biological and sequencing parameters. The recall and the precision rates have been assessed for each tool to detect mutations with varying transition/transversion ratio, allelic fraction, and coverage.
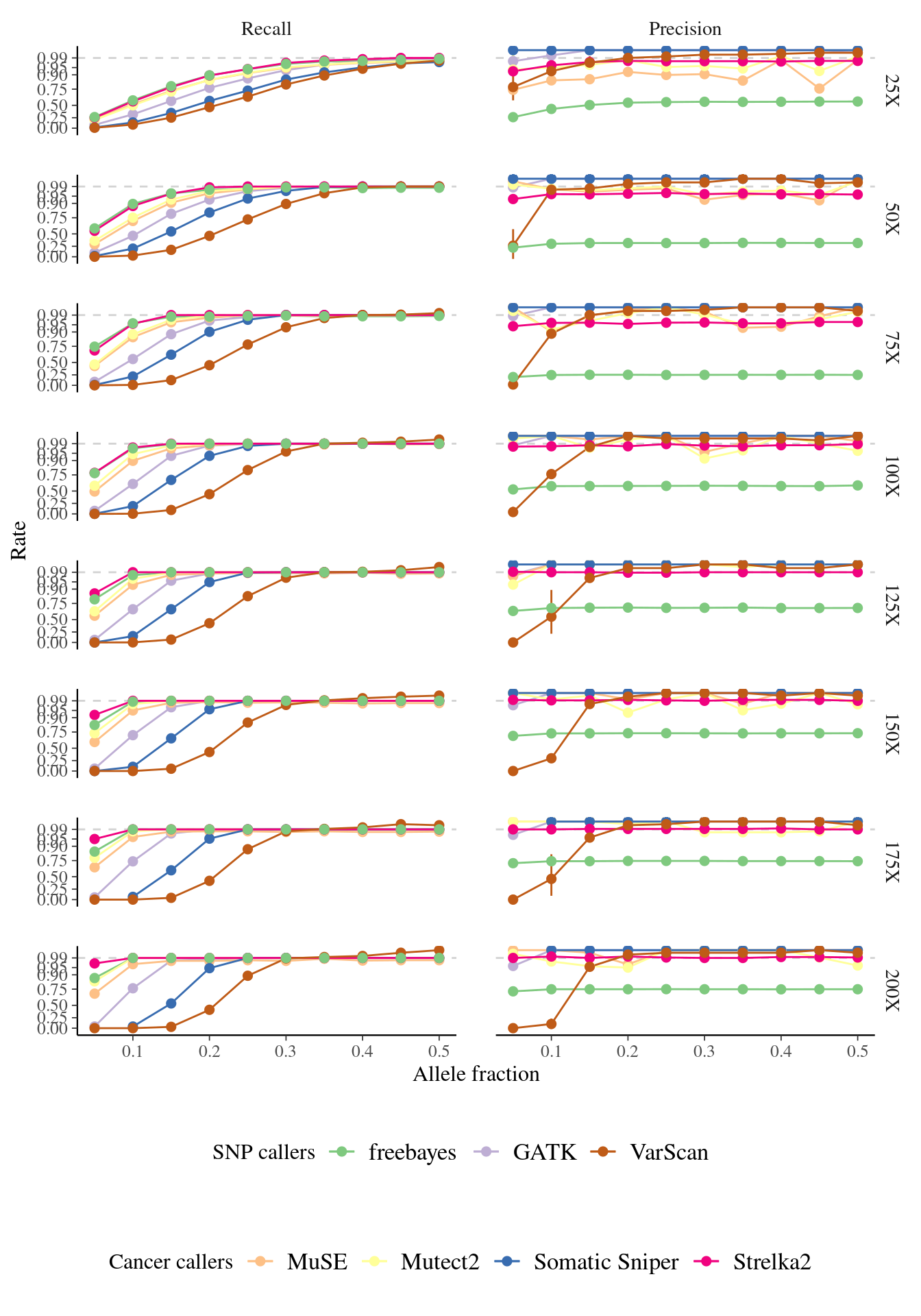
Figure 7.8: Variation in the performance of mutation detection tools with varying biological and sequencing parameters. The recall and the precision rates have been assessed for each tool to detect mutations with varying transition/transversion ratio, allelic fraction, and coverage.